Just a few decades ago, iris scanners and fingerprint-operated door locks were considered science fiction. Today, this biometric technology is part of everyday life. iPhone and iPad users enjoy the simplicity of Touch ID authentication to unlock their devices, and now facial recognition on the iPhone X. Office buildings, labs and government buildings no longer need to worry about security breaches due to lost key cards, as biometric lock systems have replaced the traditional predecessors. And, Galaxy S8 users can also access their devices with a simple glance.
A biometric mobile app can open the door to a more secure, key-free world–one where you don’t need to recall dozens of different passwords, carry a keychain or even type in a PIN. But, how does biometric security technology actually work and how is it used in biometric apps?
Types of Biometrics for Mobile Apps and Devices
Biometric mobile apps come in many forms. In fact, biometric security applications are not traditionally sold as stand-alone apps. Instead of a biometric app, biometric logins are typically integrated into a larger mobile app interface, an IoT device or even the operating system for a device that demands a high level of security.
Some of the most common biometric authentication techniques include:
- Fingerprint scans: Fingerprint scanning entered the mainstream in 2013 with Apple’s release of the iPhone 5S. It’s a very secure and reliable biometric authentication technique because each person’s fingerprints are unique, even in the case of identical twins. This form of authentication works by identifying key markers on a verified fingerprint. The more marker points you identify, the higher the security level. Then, the user’s fingerprint is captured during the login process and compared to the verified master. If all the key markers align, access is granted—providing all other conditions, such as body temperature, galvanic skin response and pulse, are within normal limits. These properties are vital for preventing users from fooling the system with a molded reproduction of the authorized user’s digit.
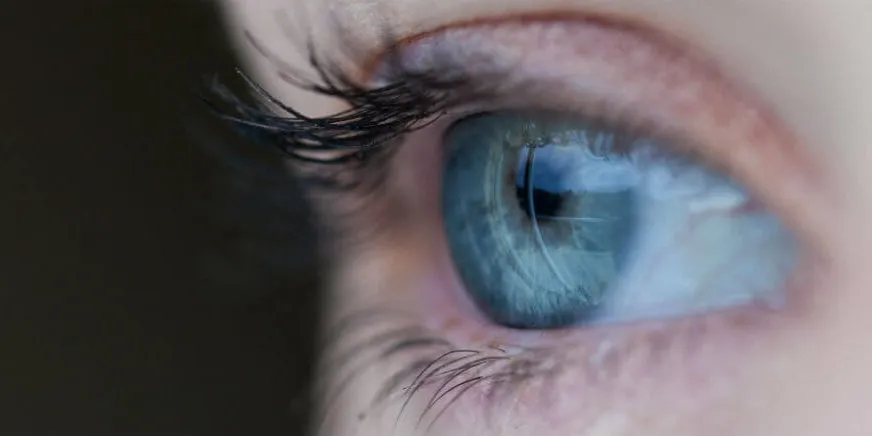
- Iris scans: The iris is said to be nearly impossible to replicate, so it’s a natural choice for biometric security applications. Each eye is unique, with different flecks and colorations. In fact, even your left and right eye are slightly different, which means the iris can allow for very accurate authentication and identification. To start the authentication process, a high-tech eye scanner maps your eye’s iris. The app identifies key marker points on the iris, with a higher number of designated marker points correlating with a higher level of security. In order to be considered a match, the eye presented during the login process must have the same marker points. The eye scanner hardware is typically configured to evaluate other properties as well, such as reflectivity and temperature, making it more challenging for a person to deceive the system.
- Facial scans: Facial recognition technology has seen major advances in recent years. In fact, many European cities are outfitted with extensive surveillance camera networks that are equipped to scan the faces of citizens, identifying suspected terrorists and individuals sought by law enforcement. This facial recognition technology is now being used in mobile devices with biometric security apps. The beauty of this biometric technology is that you don’t need a special scanner, as is required for iris scans or fingerprints; simply looking at the device’s camera input is sufficient to gather the information needed for authentication. Facial recognition technology works by laying a digital grid over an image of the individual’s face. The grid is used to evaluate the geometry of the person’s facial features, such as the distance between the eyes and the angles that form if you were to mark key locations on the face and connect the dots. Some facial scanning technology is so sophisticated that it can differentiate between identical twins. Although Galaxy S8 users have identified a major flaw: the facial recognition system can be fooled with a photo. But it’s conceivable that this fault may be remedied in the not-so-distant future.
- Voice recognition: Voice recognition technology has advanced alongside related technologies, such as natural language processing (NLP), the technology that enables Siri and Alexa to understand what the user is saying. When using a voice for authentication, the sound is converted into a digitized map of sorts, which is then compared to the master copy. Voice recognition is a bit less secure than some other biometrics, as voices can change due to an illness or allergies. It’s also relatively easy to capture an individual’s voice with a recording. Digital recordings do distort the voice, though, so developers may refine voice recognition technology to detect digitized vocal renderings. This would make it extremely challenging to trick a voice recognition-based biometrics security app.
Why is Biometric Security Better Than Other Authentication Methods?
When it comes to overall security levels, biometrics tend to lead the pack due to their inherent benefits:
- You cannot lose or forget your fingerprint, face or iris.
- Each person’s biometrics are unique.
- Your eyes, fingerprints and the geometry of your face remain constant over time.
- It’s extremely difficult—if not impossible—for another person to accurately replicate or steal the body parts used for biometric authentication.
These properties make biometric logins an ideal choice as a security measure, whether it’s integrated into a financial app or part of the two-factor authentication requirements for unlocking a device. It’s conceivable that we could soon see biometrics take the place of keys, including your house key, the key to your office and your car key/fob. Instead, the door (or vehicle) would be opened using an app that verifies your identity.
There’s a world of possibility in the realm of biometrics IoT integration, so visionary entrepreneurs are turning to innovative developers. At 7T, we take a futuristic view, focusing on some of the most rapidly-advancing areas of technology, including augmented reality, artificial intelligence and predictive analytics.
Our company is headquartered in Dallas, with regional offices in Austin and Houston, Texas. We also work with clients across the United States. If you’re ready to learn more, contact the team at 7T today.