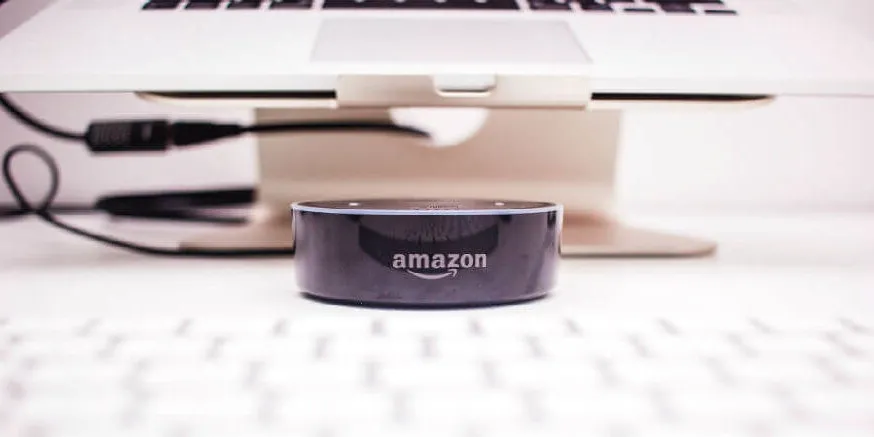
Amazon reportedly sold over 10 million Echo devices between 2014 and 2017, each equipped with Alexa—a virtual assistant that leverages natural language processing (NLP) technology to fulfill your requests. Google and Apple have also released virtual assistant-equipped IoT devices that allow users to do everything from playing a specific song, adjusting the lighting or starting their coffee maker to dispatching their Roomba. In fact, Apple’s Siri NLP capabilities are regarded as some of the most sophisticated in the industry.
As you come up with concepts for new IoT devices and gadgets, you’ll ultimately turn to an app developer who can design user-friendly applications based on your vision. But if your user is going to enjoy the maximum benefit from the device and its accompanying app, you’ll need to ensure full compatibility with virtual assistants such as Alexa and Siri. And, therein lies the problem, as IoT integration can be challenging and complex. So what points should you keep in mind as you begin the app development process?
Why Does Your App Need to Get Along With Alexa, Siri and Other VAs?
Today’s tech-centric user really expects that your IoT device (and its companion app) will be fully compatible with smart home devices such as Amazon’s Echo, Apple’s HomePod and Google Home. Full integration allows the user to issue verbal commands to the virtual assistant. The VA, in turn, interacts with the IoT device management app, which prompts the device to perform a specific task.
While a high degree of integration may be considered “standard,” actually achieving that integration can be challenging from a technical perspective. This is especially true if you’re planning to integrate with Siri, Alexa and Google Assistant.
How Do You Integrate IoT Devices With Virtual Assistants?
Each platform—Apple, Google and Amazon—has its own unique specs, platforms and processes in place to achieve integration. Technically speaking, Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant have fairly similar structures and integration processes. Google accommodates “actions,” while Amazon allows third-party developers to create “skills.” Developers must establish a server that will execute the “skill” or “action” that’s required to achieve integration. Both are compatible with the node.js server platform, which is good news for developers.
Google makes its API.AI available to developers, who are free to host their actions on any platform, including cloud servers. Amazon is a bit more restrictive, requiring developers to host their skills on an AWS Lambda server.
Once the issue of hosting is addressed, you’ll need to ensure that your skill or action aligns with the platform’s security and quality standards. Amazon is relatively permissive when it comes to skills, which are representative of the industry’s average standards. Developers must submit their skill to Amazon for a review process, which can take anywhere from two to seven days. Any and all issues will be identified, and developers are then provided with the feedback they need to remedy the issues and gain approval.
Google, on the other hand, has higher standards for action submissions. Like Amazon, though, reviewers will provide feedback to developers on what issues must be corrected in order to gain approval.
Additionally, both Amazon and Google maintain marketplaces with dozens of third-party actions and skills that are available for developers to use. This means it may be possible to leverage an existing skill or action instead of developing a new one.
The Apple MFI Certification Process for IoT Devices and Companion Apps
The process of integrating with Apple’s Siri is more complex and involved, although some may opt to postpone this integration as Apple’s HomePod currently has the smallest market share of the three key IoT home devices.
Apple integration entails an MFI review and certification process for the device hardware. Apple MFI testing is performed at an independent facility, where the technology is subjected to mechanical, electrical and stress testing. Additionally, Apple performs routine audits of manufacturing facilities that produce MFI certified devices.
Once the device is Apple MFI certified, it must be HomeKit-enabled to allow for compatibility with the HomePod. Then, once the hardware is approved, you’ll be tasked with fixing any issues with the device’s companion app. Needless to say, Apple integration is an intensive, complicated process that involves both hardware and software.
Selecting a Developer Who Can Ensure IoT Integration With VAs
Natural language processing has prompted a revolution, paving the way to more intuitive and natural interactions with technology. Alexa and Siri NLP technology has truly transformed the way in which we interact with our devices. As such, it’s important that your IoT devices are compatible with the most popular virtual assistants. But not every developer has experience with the technology and processes required for a smooth integration.
At 7T, we excel at IoT integration. In fact, we focus on some of the most cutting-edge technologies, which means our team is well-positioned to take on a wide variety of projects. This includes everything from natural language processing and artificial intelligence to predictive analytics, augmented reality, virtual reality and beyond.
7T is based in Dallas, with regional offices in Austin and Houston. But our clientele is scattered across the country, so no matter where you’re located, our team is happy to assist with your next development project. Contact us today to discuss your ideas for an IoT device companion app.